Understanding Uncertainty in AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved, transforming industries and reshaping how we interact with technology. However, as AI systems become more complex and integrated into critical decision-making processes, the concept of uncertainty in AI has gained significant attention. Understanding and managing this uncertainty is crucial to ensuring the reliability and safety of AI applications.
What is Uncertainty in AI?
Uncertainty in AI refers to the lack of certainty or predictability in the outcomes produced by AI models. This can arise from various sources, including incomplete data, ambiguous information, model limitations, or inherent randomness in real-world scenarios. Unlike traditional deterministic systems, where inputs lead to predictable outputs, AI systems often operate under probabilistic frameworks that account for uncertainties.
Sources of Uncertainty
- Data Uncertainty: Often referred to as aleatoric uncertainty, this arises from noise or variability within the data itself. For instance, sensor errors or incomplete datasets can introduce significant variability into an AI model’s predictions.
- Model Uncertainty: Also known as epistemic uncertainty, this occurs due to a lack of knowledge about which model best represents the underlying data-generating process. It often results from limited training data or overly simplistic models.
- Environmental Uncertainty: This type of uncertainty stems from unpredictable changes in external conditions that affect how an AI system performs over time.
The Impact of Uncertainty
The presence of uncertainty can significantly impact the performance and trustworthiness of AI systems. In high-stakes applications such as autonomous driving or medical diagnosis, failing to adequately address uncertainty can lead to erroneous decisions with potentially severe consequences. Therefore, it is essential for developers and stakeholders to understand and mitigate these uncertainties effectively.
Managing Uncertainty
A variety of techniques have been developed to manage uncertainty in AI:
- Probabilistic Models: These models explicitly account for uncertainties by representing predictions as probability distributions rather than single-point estimates.
- Ensemble Methods: By combining multiple models’ outputs, ensemble methods help reduce model uncertainty and improve predictive accuracy.
- Sensitivity Analysis: This approach assesses how changes in input variables affect output predictions, helping identify areas where uncertainties have a significant impact.
- User Feedback Loops: Incorporating user feedback allows models to learn from their mistakes and adjust their predictions over time.
The Future of Uncertainty Management in AI
The ongoing research into understanding and managing uncertainty will be pivotal for future advancements in AI technology. As algorithms become more sophisticated and datasets grow larger and more complex, developing robust methods for handling uncertainty will be key to building trustworthy artificial intelligence systems that can operate safely across diverse environments.
The challenge lies not only in improving technical solutions but also in fostering transparency around how these systems handle uncertain situations. By doing so, developers can build greater confidence among users while paving the way for broader adoption across various sectors worldwide.
Understanding and Managing Uncertainty in AI: Key Questions Answered
- What is uncertainty in AI?
- Why is uncertainty important in AI?
- What are the sources of uncertainty in AI?
- How does data uncertainty impact AI models?
- What is model uncertainty and how does it affect AI systems?
- How can environmental uncertainty influence the performance of AI applications?
- What are some common techniques for managing uncertainty in AI?
- Why is addressing uncertainty crucial in high-stakes AI applications like autonomous driving and healthcare?
- How can users build trust in AI systems despite inherent uncertainties?
What is uncertainty in AI?
Uncertainty in AI refers to the inherent unpredictability or lack of certainty in the outcomes and decisions made by artificial intelligence systems. This uncertainty can stem from various sources, such as incomplete or noisy data, limitations in the models themselves, and unpredictable changes in the environment where the AI operates. Unlike traditional deterministic systems that produce fixed results from given inputs, AI systems often use probabilistic models to handle uncertainties, providing outputs that reflect a range of possible outcomes rather than a single definitive answer. Understanding and managing this uncertainty is crucial for ensuring that AI applications remain reliable and effective, particularly in high-stakes areas like healthcare and autonomous vehicles.
Why is uncertainty important in AI?
Uncertainty is crucial in AI because it directly influences the reliability and safety of AI systems, especially when they are used in decision-making processes. In real-world applications, AI systems often encounter incomplete or ambiguous data, making it essential to understand and manage the inherent uncertainties. By accounting for uncertainty, AI models can provide probabilistic predictions that reflect the confidence level in their outputs. This allows for more informed decision-making, particularly in high-stakes scenarios such as healthcare diagnostics or autonomous driving, where inaccurate predictions could lead to significant consequences. Effectively addressing uncertainty helps build trust in AI technologies and ensures that they operate safely and efficiently across various environments.
What are the sources of uncertainty in AI?
Uncertainty in AI arises from several key sources, each contributing to the unpredictability of AI models and their outcomes. One primary source is data uncertainty, also known as aleatoric uncertainty, which stems from noise or variability within the data itself, such as sensor errors or missing information. Another significant source is model uncertainty, or epistemic uncertainty, which occurs due to a lack of knowledge about the most appropriate model to accurately represent the data-generating process. This often results from limited training data or overly simplistic models that fail to capture complex patterns. Additionally, environmental uncertainty arises from unpredictable changes in external conditions that can affect an AI system’s performance over time. Understanding these sources is crucial for developing robust AI systems capable of making reliable predictions in diverse and dynamic environments.
How does data uncertainty impact AI models?
Data uncertainty, often referred to as aleatoric uncertainty, significantly impacts AI models by introducing variability and noise into their predictions. This type of uncertainty arises from the inherent imperfections in data collection processes, such as sensor errors, incomplete datasets, or ambiguous information. When AI models are trained on data with high levels of uncertainty, their ability to make accurate and reliable predictions can be compromised. This is because the models may struggle to distinguish between meaningful patterns and random noise within the data. As a result, addressing data uncertainty is crucial for improving the robustness and accuracy of AI systems. Techniques such as probabilistic modeling and data augmentation are often employed to help mitigate these effects by providing more comprehensive representations of the underlying uncertainties in the data.
What is model uncertainty and how does it affect AI systems?
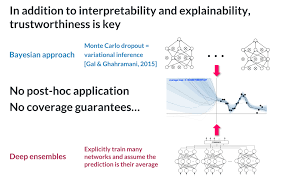
Model uncertainty, also known as epistemic uncertainty, arises from a lack of knowledge about the most appropriate model to accurately represent the underlying data-generating process. This type of uncertainty is particularly prevalent when there is limited training data or when models are overly simplistic. In AI systems, model uncertainty can significantly affect decision-making and predictions, leading to less reliable outcomes. For instance, if an AI system is tasked with diagnosing medical conditions based on patient data, model uncertainty might result in incorrect diagnoses due to the system’s inability to fully capture all relevant patterns in the data. Addressing model uncertainty involves employing techniques such as ensemble methods or Bayesian approaches that allow for better estimation and management of these uncertainties, ultimately enhancing the system’s robustness and reliability.
How can environmental uncertainty influence the performance of AI applications?
Environmental uncertainty can significantly impact the performance of AI applications by introducing unpredictable variables that the system may not be equipped to handle. This type of uncertainty arises from changes in external conditions, such as fluctuations in weather, variations in lighting, or unexpected obstacles in physical environments. For instance, an autonomous vehicle’s AI system might struggle to accurately interpret its surroundings during sudden weather changes like fog or heavy rain, leading to potential errors in navigation and decision-making. Similarly, an AI-powered drone operating in a dynamic environment with shifting wind patterns may experience difficulties maintaining stability and accuracy. To mitigate these challenges, AI systems must be designed with robust adaptability and real-time data processing capabilities to account for and adjust to environmental uncertainties effectively.
What are some common techniques for managing uncertainty in AI?
Managing uncertainty in AI involves several techniques designed to enhance the reliability and accuracy of AI models. One common approach is the use of probabilistic models, which represent predictions as probability distributions instead of single-point estimates, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of potential outcomes. Ensemble methods are also widely used; these combine outputs from multiple models to reduce individual model uncertainty and improve overall predictive performance. Sensitivity analysis plays a crucial role by examining how variations in input data can impact model outputs, helping identify areas where uncertainty has significant effects. Additionally, incorporating user feedback loops allows AI systems to learn from their mistakes and adjust predictions over time, thereby reducing uncertainty through continuous refinement. These techniques collectively contribute to building more robust and trustworthy AI systems capable of operating effectively in uncertain environments.
Why is addressing uncertainty crucial in high-stakes AI applications like autonomous driving and healthcare?
Addressing uncertainty is crucial in high-stakes AI applications such as autonomous driving and healthcare because these fields demand high levels of accuracy and reliability to ensure safety and effectiveness. In autonomous driving, uncertainty can arise from unpredictable road conditions, sensor inaccuracies, or unexpected behavior from other drivers. If not properly managed, these uncertainties can lead to incorrect decision-making by the AI system, potentially resulting in accidents. Similarly, in healthcare, AI systems assist with diagnoses and treatment plans where any uncertainty in data interpretation or model predictions could lead to misdiagnoses or inappropriate treatments. By effectively addressing uncertainty, AI systems can provide more reliable outputs, reduce risks, and enhance trust among users and stakeholders in these critical areas.
How can users build trust in AI systems despite inherent uncertainties?
Building trust in AI systems, despite their inherent uncertainties, involves a combination of transparency, communication, and user engagement. Developers should prioritize making AI systems as transparent as possible by clearly explaining how decisions are made and what factors contribute to outcomes. Providing users with insights into the limitations and potential uncertainties of the system can foster informed trust. Additionally, incorporating feedback mechanisms allows users to report inaccuracies or unexpected behavior, which can be used to refine and improve the models over time. Regular updates and open communication about improvements and ongoing challenges also help build confidence in the system’s reliability. By actively involving users in the process and addressing their concerns, trust in AI systems can be strengthened even when uncertainties are present.