The Intersection of Robotics and Artificial Intelligence
In recent years, the fields of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) have seen tremendous growth and development. These two areas, while distinct, are increasingly intersecting to create innovative solutions that are transforming industries and everyday life.
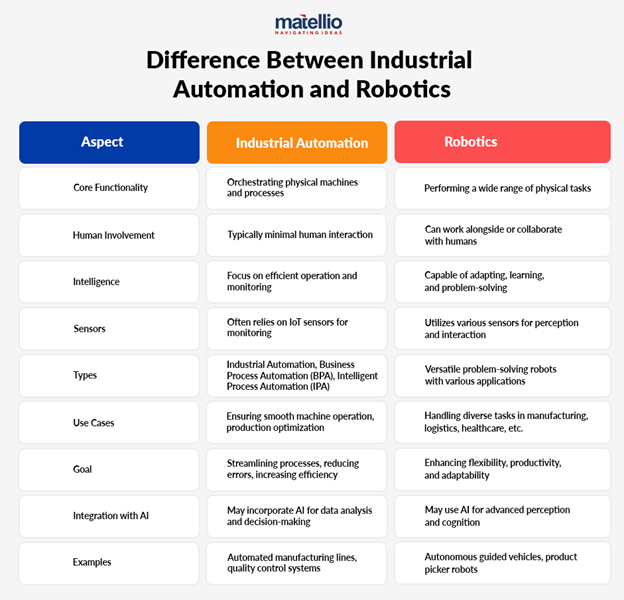
Understanding Robotics
Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, and application of robots. Robots are machines capable of carrying out a series of actions automatically, often programmable by a computer. They can be autonomous or semi-autonomous and are used in various sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, and even space exploration.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. AI involves learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using the information), reasoning (using rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction. AI technologies include machine learning, natural language processing, speech recognition, and vision systems.
The Synergy Between Robotics and AI
When robotics is combined with AI technologies, robots become more intelligent and capable. This synergy enables robots to perform complex tasks that require decision-making abilities similar to those of humans. For example:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars use a combination of robotics for navigation and AI for processing vast amounts of data from sensors to make real-time driving decisions.
- Healthcare Assistants: Robots equipped with AI can assist in surgeries with precision or provide companionship to patients while monitoring their health conditions.
- Manufacturing Automation: In factories, AI-powered robots can adapt to new tasks without human intervention by learning from their environment.
The Impact on Industries
The integration of robotics and AI is revolutionizing industries by enhancing productivity, improving safety standards, reducing operational costs, and enabling innovation. In manufacturing, smart factories use robotic systems that communicate with each other to optimize production lines. In agriculture, drones equipped with AI can analyze crop health data in real-time for better yield management.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the benefits, there are challenges associated with the adoption of robotics and AI. Ethical considerations around job displacement due to automation need addressing. Additionally, ensuring data privacy and security in AI systems is paramount as they become more integrated into daily life.
The Future Outlook
The future holds immense potential for further advancements at the intersection of robotics and artificial intelligence. As technology continues to evolve rapidly, we can anticipate more sophisticated applications that will redefine how humans interact with machines across various domains.
Ultimately, leveraging these technologies responsibly will be key to unlocking their full potential while addressing societal impacts effectively.
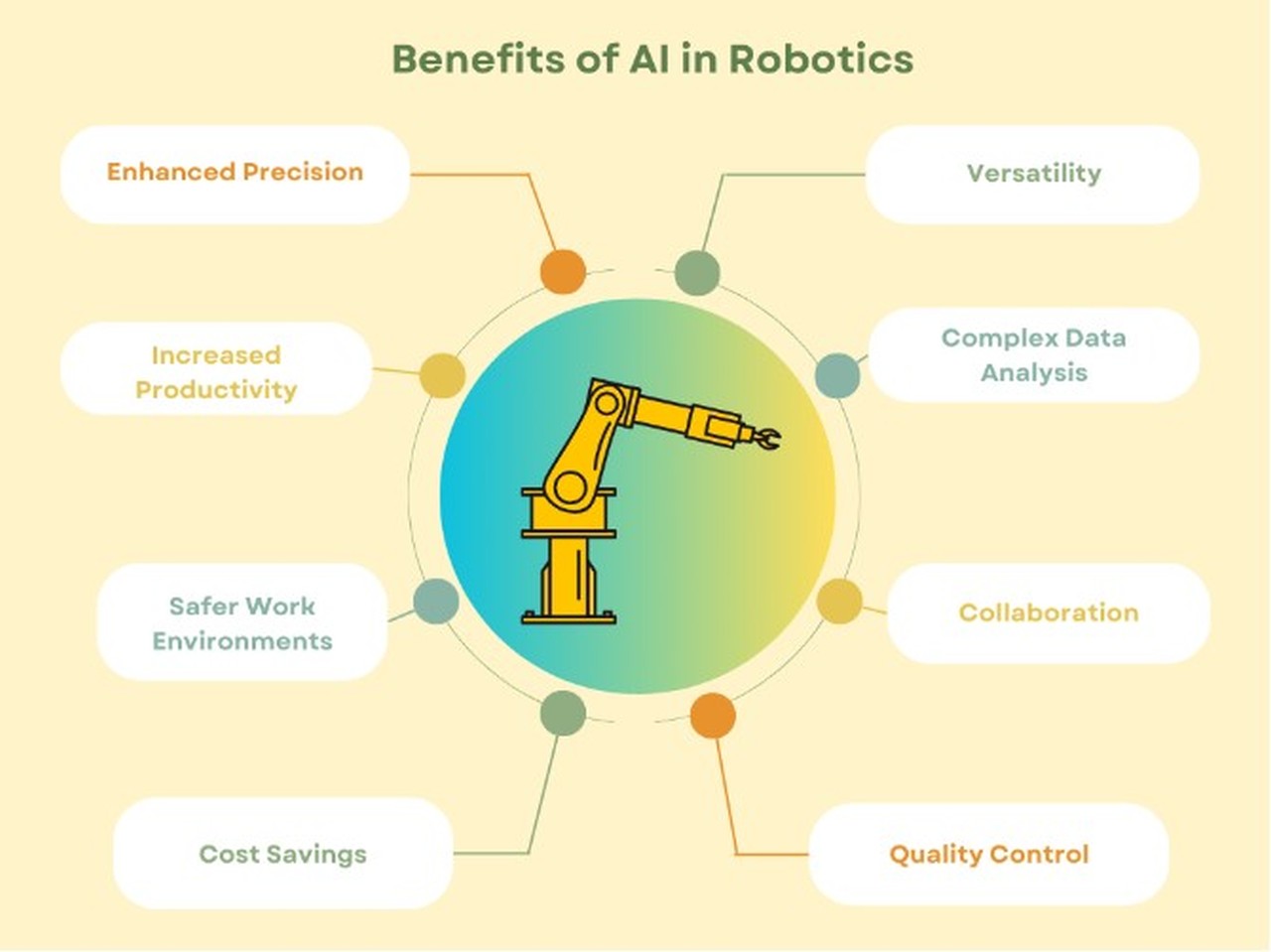
5 Key Benefits of Robotics and AI: Boosting Efficiency, Precision, Safety, Innovation, and Cost Savings
Challenges of Robotics and AI: Job Displacement, Ethical Concerns, Tech Dependency, and Inequality
Increased efficiency
The integration of robotics and artificial intelligence significantly boosts efficiency by streamlining processes and automating tasks across various industries. By leveraging these advanced technologies, businesses can achieve higher productivity levels as robots and AI systems handle repetitive or complex tasks with precision and speed. This not only reduces the likelihood of human error but also frees up human resources to focus on more strategic, creative, and value-added activities. In manufacturing, for instance, AI-powered robots can work tirelessly around the clock, optimizing production lines and ensuring consistent quality. Similarly, in sectors like logistics and supply chain management, AI algorithms enhance route planning and inventory management, resulting in faster delivery times and reduced operational costs. Overall, the increased efficiency brought about by robotics and AI enables organizations to maximize output while maintaining high standards of quality and service.
Enhanced precision
Enhanced precision is one of the most significant advantages of integrating robotics with artificial intelligence. Robots equipped with AI can execute tasks with a level of accuracy that often surpasses human capabilities. This is particularly beneficial in fields requiring meticulous attention to detail, such as surgery, manufacturing, and quality control. In surgical procedures, AI-powered robotic systems can perform complex operations with remarkable precision, reducing the risk of human error and improving patient outcomes. In manufacturing, robots can consistently produce components with exact specifications, ensuring high-quality products while minimizing waste. This unparalleled level of precision not only enhances efficiency but also opens up new possibilities for innovation across various industries.
Improved safety
One significant advantage highlighted in the discussion of robotics and artificial intelligence is the improved safety they bring to various industries. AI-powered robots are adept at handling hazardous or repetitive tasks that pose risks to human workers. By delegating such tasks to robots, organizations can significantly reduce the potential for workplace accidents and injuries, ultimately enhancing overall safety standards in the workplace. This shift not only safeguards human employees from dangerous environments but also allows them to focus on more complex and strategic responsibilities, leading to a more efficient and secure work environment.
Innovation catalyst
The integration of robotics and artificial intelligence serves as an innovation catalyst, propelling advancements across industries by driving technological progress. By combining the capabilities of robotics with the intelligence of AI, new solutions and applications emerge that revolutionize traditional processes and open up possibilities for unprecedented efficiency and creativity. This synergy not only enhances existing practices but also paves the way for groundbreaking developments that shape the future of various sectors, pushing the boundaries of what is achievable through cutting-edge technology.
Cost savings
Adopting robotics and artificial intelligence solutions offers significant cost savings by automating repetitive tasks and optimizing processes. By integrating robots and AI into operations, businesses can reduce labor costs, minimize errors, and increase efficiency. These technologies allow for 24/7 operation without the need for breaks, leading to higher productivity levels. Furthermore, AI-driven analytics can identify inefficiencies and suggest improvements, streamlining workflows and reducing waste. Over time, these efficiencies translate into substantial operational cost reductions, providing a competitive edge in various industries.
Job Displacement
The rise of robotics and artificial intelligence has brought significant advancements, but it also poses the challenge of job displacement. As automation becomes more prevalent, many tasks traditionally performed by humans are now being handled by machines, leading to potential job losses in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and even customer service. This shift raises concerns about increasing unemployment rates and highlights the urgent need for retraining programs to help workers transition into new roles. By investing in education and skill development, society can better prepare its workforce for the evolving job landscape, ensuring that individuals can adapt to technological changes rather than being left behind.
Ethical Dilemmas
As robotics and artificial intelligence systems become increasingly autonomous, they bring with them a host of ethical dilemmas that require careful consideration and regulation. One major concern is accountability: when an AI system makes a decision or a robot takes action, it can be challenging to determine who is responsible for the outcomes, especially if they are negative. Additionally, AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate or even exacerbate biases present in their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Privacy is another critical issue, as these technologies often rely on vast amounts of data to function effectively, raising concerns about how personal information is collected, stored, and used. Addressing these ethical challenges necessitates the development of comprehensive regulations and guidelines to ensure that the deployment of robotics and AI aligns with societal values and protects individual rights.
Dependency on Technology
Dependency on technology, particularly robotics and artificial intelligence, can lead to overreliance that poses significant risks. In the event of system failures or compromises, there is a potential for disrupting critical services or processes essential for daily operations. This vulnerability highlights the importance of maintaining a balance between leveraging advanced technologies for efficiency and ensuring robust contingency plans to mitigate the impact of any unforeseen incidents.
Inequality Issues
The integration of advanced robotics and artificial intelligence technologies into various sectors has the potential to widen existing societal inequalities if these innovations are not made affordable and accessible to all segments of the population. As these technologies become integral to industries such as healthcare, education, and manufacturing, those with limited access may find themselves at a significant disadvantage. This disparity can lead to a concentration of economic and social benefits among wealthier individuals or regions that can afford these technologies. To mitigate this risk, it is crucial for policymakers and industry leaders to develop strategies that promote equitable distribution and access, ensuring that advancements in robotics and AI contribute to reducing inequality rather than exacerbating it.